Varicose veins is not only an aesthetic problem. We are talking about a serious threat to the health and even life. At the first sign of the disease should consult a doctor and start treatment.
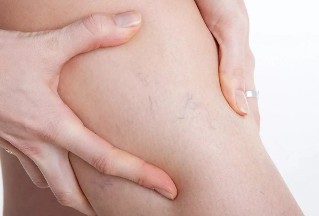
Let's see, what treatments can offer medicine.
A modern approach to the treatment of varicose veins
It is difficult to underestimate the prevalence of this pathology, because according to statistics it affects about 75% of women and 60% men. And it is only among the inhabitants of developed countries. In order to explain the cause of varicose veins, you should have an idea about the structure of the veins of the lower extremities. Venous blood in our legs constantly moves upwards, overcoming the laws of gravity, for the implementation of this process, veins are equipped with special valves that prevent the liquid to fall down in between the jolts of the heart. Disruption of this mechanism provokes the reverse current of venous blood, and because of the greater number of the veins dilate, decreases their tone.
The first stage of varicose vein disease usually goes away without special symptoms, except that accompanied by mild discomfort in the legs, and "heaviness" in the evening. You may notice that the legs get tired even after short walks. For a second sub-compensation stage, these features are enhanced and appear aching pain, swelling, tingling in legs, cramps.
Third, de-compensatory stage is characterized by irreversible changes of the skin of the shins:
- edema not fully go away even after sleep;
- hyperpigmentation;
- indurate — protruding seal skin.
Thus the skin becomes easily vulnerable, possible varicose eczema and, as the finale of trophic disorders, ulcers. Ignoring the disease is also facing such complications as thrombophlebitis and thromboembolism.
The sooner treatment begins, the more hopeful will be the prognosis. But after success you must adjust your lifestyle, leaving time for preventive procedures.
Suspected varices should be a reason for early visits to the doctor, which will help to identify the disease and determine its stage.
Diagnosis — the first step to recovery
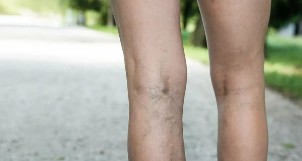
In particular, the practitioner interviewing the patient is necessary to collect anamnesis. Continue to be a standard inspection and palpation of the affected areas. For a more detailed and accurate diagnostic use of ultrasound duplex angio-scanning with color mapping of the bleeding. The procedure is as simple ultrasound with the only difference that in addition to the two-dimensional images the doctor sees the speed and direction of movement mapping of blood flow in the vessels. Modern ultrasound machines can accurately determine the idle valve vein segments with abnormal direction of blood flow, to precisely mark the projection on the skin.
Once the diagnosis is clarified, it's time to start taking action to get rid of varicose veins.
Conservative treatment of varicose veins
With non-surgical methods can prevent, inhibit or alleviate the disease. As the main method of treatment they are used only in the case where operation is not possible.
Conservative methods include:
- Compression therapy, i.e. the use of special compressive underwear or elastic bandages. Their impact constricts the veins, thus facilitating the operation of the valve and improving blood flow. Effectiveness of compression therapy has been proven by numerous studies. There are contraindications among them atherosclerosis, aortoarteritis, inflammatory skin diseases and others.
- Drug therapy involves the use of medications such as for oral administration and for local applications (in the form of ointments). To the groups of drugs for the treatment of varicose veins in the legs include venotonic and anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants (blood thinners). Necessary medication the doctor prescribes individually. It is important to remember that everyone has contraindications. For example, most tablets venotonic cannot be taken in early pregnancy and when breast-feeding. And when taking anticoagulants need regular blood tests for blood clotting.
As the primary treatment in the absence of any obstacles and contraindications appoint one of the options of surgical treatment.
Traditional surgery (venectomy)
Currently used only in specific cases related to the special structure of veins or complicated course of the disease, for example, in various forms of acute thrombophlebitis.
The operation consists in the ligation of the confluence of the trunk of the affected saphenous vein in the deep system (crossectomy) and subsequent mechanical removal of the barrel. Manipulation is performed under General anaesthetic or using a spinal anesthesia and lasts 1-2 hours. Due to the high incidence of postoperative complications — hematomas in places of removal of the trunk, prolonged pain, skin neuralgia and paresthesias (numbness) in recent years, the traditional surgical intervention gives way to a modern method. These include endo-venous laser photocoagulation.
After surgery recommend regular physical activity no significant loads during one-half months shown compression therapy.
In addition to this treatment method, there are other, more gentle ways to get rid of varicose veins on the legs.
Minimally invasive techniques
There are several types of minimal invasive methods for treatment of varicose veins. On the basis of data about the patient and the characteristics of the disease cures, the doctor takes a decision on whether to conduct one of the procedures.
Endo-venous laser photocoagulation
Operation endo-venous laser treatment has become the method of treatment of varicose disease of any severity. Neither the severity of venous insufficiency, nor the thickness of the venous lumen of the barrel at the present time are not constraints for endo-venous laser treatment. This was possible thanks to the use of the following tools:
- two-wave lasers with one wave absorption by hemoglobin and the second vascular wall;
- the radial fibers, which provides treatment around the entire circumference of the inner surface of the vein;
- automatic pump that allows to pump the anesthetic solution around the vein providing pain relief, reducing the diameter of the vein, and protection of adjacent tissues.
Special preparation for endo-venous laser treatment is not necessary. Before the operation is necessarily performed ultrasound duplex scanning. It is also necessary to give blood for the standard set of preoperative tests: General, biochemical, coagulogram.
During the procedure, the doctor puncture the affected vein, and then insert a thin (1 mm thick) catheter with a light guide. This whole process, as well as the position of the light guide in Vienna and further "brewing" Vienna is controlled by intraoperative ULTRASONIC apparatus. The operation lasts about 40 minutes and requires only local anesthesia.

After surgery hospital stay is not required, the patient must wear a compression garment for 3-5 days, and within a couple of weeks recommended daily relaxing walks.
Radiofrequency ablation
The operation is essentially similar to laser coagulation. The only difference is that on the walls of veins for her "closure" and subsequent resorption effect of radio frequency radiation. Special training, in addition to standard preoperative, is not required.
At the present time in connection with the improvement of laser systems no advantages over the endo-venous laser photocoagulation, radiofrequency ablation has not. However, the procedure is more expensive due to the high price of the waveguides.
Operation can't be done during pregnancy and lactation, atherosclerosis of arteries of the lower extremities and the inability of subsequent physical activity.
Possible complications and a complex of restorative measures during the rehabilitation period is similar to the previous procedure.
Mini-phlebectomy
The principle of operation is to remove the tributaries and components of the vein through the puncture or incision in the skin using special tools. It is used isolated varicose tributaries or as an additional procedure after laser coagulation, radiofrequency ablation, and surgical phlebectomy.
Training is similar to previous procedures — a standard set of tests and an ultrasound scan of the veins. Contraindications — pregnancy and lactation, acute infectious diseases, thrombophlebitis, impaired motor activity, pathology of blood clotting.
The duration of the mini-phlebectomy is 20-40 minutes, during rehabilitation it is necessary to wear compression stockings.
Sclerotherapy
The technique is non-surgical treatment of varicose veins ideal for advanced varicose veins, and for aesthetic purposes — for the destruction of vascular "stars" and "veins".
Contraindications are thrombosis, Allergy, infection, pregnancy and lactation, the inability to perform accurate injection.
Sclerotherapy involves injection into a vein puncture using a special substance that "glues" the wall of the vessel that occurred after its resorption. One of the latest innovations — method of foam-foam, which provides the use of a foam form of the drug. Thus it is the least washed out with blood, which makes it possible to reduce the concentration and quantity of substance at higher efficiency. The operation is performed without anesthesia, so as to puncture requires only a thin insulin needle.
Side-effects of sclerotherapy include pigmentation, which appears in the course sklerozirovanie of Vienna. In some cases, incomplete bonding of Vienna, which will require re-treatments.
After sclerotherapy, you need to wear a compression garment and avoid strenuous activities and high temperatures (for example, when visiting the sauna).
The cost of sclerotherapy depends on the volume. For removal of large varicose trunks sclerotherapy is now almost never used. And sclerotherapy small venous nodes or networks will cost from 7,000 to 20,000 rubles.
With the development of medicine the struggle with varicose veins in the legs have moved from the category of "hundred years war" in the category of "quick wins". Sophisticated surgical techniques have given way to minimally invasive procedures that are safer and effective. Today varicose veins is not a sentence, but the only reason to see a specialist.























